Description
Details
Cultivate T cells to win the fight
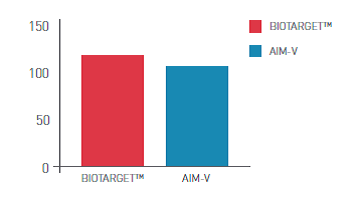
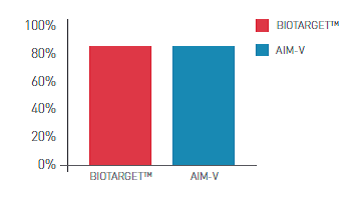
BIOTARGET™ is a serum-free, xeno-free medium developed and optimized specifically for activation and expansion of PBMC - peripheral blood mononuclear cells (lymphocytes and monocytes). This medium is available in many customized packaging configurations.
BIOTARGET™ Advantages
- Xeno-free, chemically defined
- High viability and expansion rates
- No added cytokines
- Comprehensive validation studies
- Produced under cGMP conditions
- Customized packaging
Applications
- LAK, TIL, CAR-T cell generation and expansion
- T cell activation
- Cytokine production
- Culturing peripheral blood mononuclear cells (lymphocytes and monocytes)
- T cell subset-specific responses
- Natural killer (NK) cell generation and tumor recognition
- Macrophage activation
Specifications
Specifications
| QTY | 500 mL |
|---|---|
| Glutamine | No Glutamine |
| Storage Conditions | 2-8°C |
| Shipping Conditions | Cold Pack |
References
references
- М.S. Zhunussova, et. al. Comparative analysis of impact of tumour antigen preparation methods on human dendritic cells priming and efficient cytokine-induced killer cells activation in vitro. Experimental Biology, 2021. https://doi.org/10.26577/eb.2021.v86.i1.08
- L. Olender, et al. Cyclosporine H Improves the Multi-Vector Lentiviral Transduction of Murine Haematopoietic Progenitors and Stem Cells. Sci Rep 10, 1812 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-58724-x
- F. Alfei, et al. TOX reinforces the phenotype and longevity of exhausted T cells in chronic viral infection Nature 571, 265–269 (2019) doi:10.1038/s41586-019-1326-9
- V. l. Eisenberg et al. Targeting Multiple Tumors Using T-Cells Engineered to Express a Natural Cytotoxicity Receptor 2-Based Chimeric Receptor. Frontiers in Immunology, 29 September 2017
- S. Janik et al. Diverse Regulation of Vitamin D Receptor Gene Expression by 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D and ATRA in Murine and Human Blood Cells at Early Stages of Their Differentiation. International Journal of Molecular Science. 2017, 18(6), 1323
- K. Shamalov et al. The mutational status of p53 can influence its recognition by human T-cells. OncoImmunology, Volume 6, 2017 - Issue 4
- R. Meir et al. Nanomedicine for Cancer Immunotherapy: Tracking Cancer-Specific T-Cells in Vivo with Gold Nanoparticles and CT Imaging. ACS Nano, 2015, 9 (6), pp 6363–6372
- O. Betzer et al. In-vitro Optimization of Nanoparticle-Cell Labeling Protocols for In-vivo Cell Tracking Applications. Scientific Reports volume 5, Article number: 15400, 2015
- Y. Fisher et al. Th1 Polarization of T Cells Injected into the Cerebrospinal Fluid Induces Brain Immunosurveillance. The Journal of Immunology, vol. 192 no. 1 92-102, 2014.
- Y. Tal et al. An NCR1-based chimeric receptor endows T-cells with multiple anti-tumor specificities. Oncotarget, 5(21): 10949–10958, 2014.
- Y. Ilan, H.L. Weiner. Combination Therapy of Beta-Glycolipids and Antibodies for the Treatment of Immune-Related Disorders. US 20140255420 A1, 2014.
- C. Ankri et-al. Human T Cells Engineered To Express a Programmed Death 1/28 Costimulatory Retargeting Molecule Display Enhanced Antitumor Activity. The Journal of Immunology vol. 191 no. 8 4121-4129, 2013.
- I. Llaudó et al. Do drug transporter (ABCB1) SNPs and P-glycoprotein function influence cyclosporine and macrolides exposure in renal transplant patients? Results of the pharmacogenomic substudy within the symphony study. Transplant International Volume 26, Issue 2, pages 177–186, February 2013.
- Y. Porat. Method for using directing cells for specific stem/progenitor cell activation and differentiation. US 8956870 B2, 2013 .
- I. Daniel-Meshulam et al. Enhanced antitumor activity mediated by human 4-1BB-engineered T cells. International Journal of Cancer, Volume 133, Issue 12, pages 2903–2913, 2013.
- I. Llaudó Vallmajor et al. Impact of small molecules immunosuppressants on P-glycoprotein activity and T-cell function. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, vol. 15, num. 3, p. 407-419, 2012 .
- A. Nemirovski et al. Active Aβ vaccination fails to enhance amyloid clearance in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease with Aβ42-driven pathology. Journal of Neuroimmunology, Volume 247, Issues 1-2, Pages 95–99, 2012 .
- S. Abuybul et al. TGF-β signaling through SMAD2/3 induces the quiescent microglial phenotype within the CNS environment. Glia Volume 60, Issue 7, pages 1160–1171, July 2012.
- A. Monsonego, T-cell therapy to neurodegenerative diseases. US Application, US20130280224A1
- E. Elinav, N. Adam, T. Waks and Z. Eshhar. Amelioration of Colitis by genetically engineered murine regulatory T cells redirected by antigen-specific chimeric receptor. Gastroenterology 136(5): 1721-1731, 2009.
- Yang-Ming Tseng, Sheng-Yi Chen, Chien-Hung Chen, et al.,. Effects of Alcohol-Induced Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cell (PBMC) Pretreated Whey Protein Concentrate (WPC) on Oxidative Damage. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 56 (17): 8141–8147, 2008.
- Q. Leng, Z. Bentwich and G. Borkow. Increased TGF-ß, Cbl-b and CTLA-4 levels and immunosuppression in association with chronic immune activation. International Immunology 18(5): 637-644, 2006.
- D. Melamed, O. Messika, L. Glass-Marmor and A. Miller. Modulation of matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) secretion in B lymphopoiesis. International Immunology 18(9):1355-1362, 2006.
- C. Rabinowitz and B. Rinkevich. Epithelial cell cultures from Botryllus schlosseri palleal buds: accomplishments and challenges. Methods in Cell Science 25 (3-4), 2004.
- F. Martí, E. Bertran, M. Llucià, et al., Platelet factor 4 induces human natural killer cells to synthesize and release interleukin-8. Journal of Leukocyte Biology 72: 590-597, 2002.
- A. Bishara, R. Malka, C. Brautbar, et al., Cytokine production in human mixed leukocyte reactions performed in serum-free media. Journal of Immunological Methods 215 (1-2): 187-190, 1998.
- G. Kampen, L. Poulsen, C. Reimert and P. Skov. A method for production and determination of histamine releasing activity from human peripheral blood mononuclear cell. Journal of Immunological Methods 210(2): 185-193, 1997.
- S. Morecki, Y. Gelfand, S. Levi, et al., Activated long-term peripheral blood cultures as preparation for adoptive alloreactive cell therapy in cancer patients. Journal of Hematotherapy, 6 (2):115-124, 1997.
- Malka R.; Brautbar C.; Kedar E.; et al., Human mixed leukocyte reaction (MLR) performed in serum-free media and serum-containing medium. Human immunology 44(1) : 137, 1995.
Documentation
Materials Safety Data Sheet
Manuals and Protocols
Product Literature
Certificate of Analysis
Certificates of Analysis (COA's) describe quality control data for specific product lots.
COA's can be downloaded from Sartorius's Certificates Portal.
For certificates issued before November 15, 2021, please enter below the product lot number and click search.
COA's can be downloaded from Sartorius's Certificates Portal.
For certificates issued before November 15, 2021, please enter below the product lot number and click search.
If your search does not return any results, please contact us for assistance.